The inframesocolic space also contains paracolic gutters which are peritoneal recesses that are inferolateral extensions of their corresponding inframesocolic spaces on the posterior abdominal wall lateral to the ascending and descending colon respectively.
Left paracolic gutter ct.
The left lateral paracolic gutter.
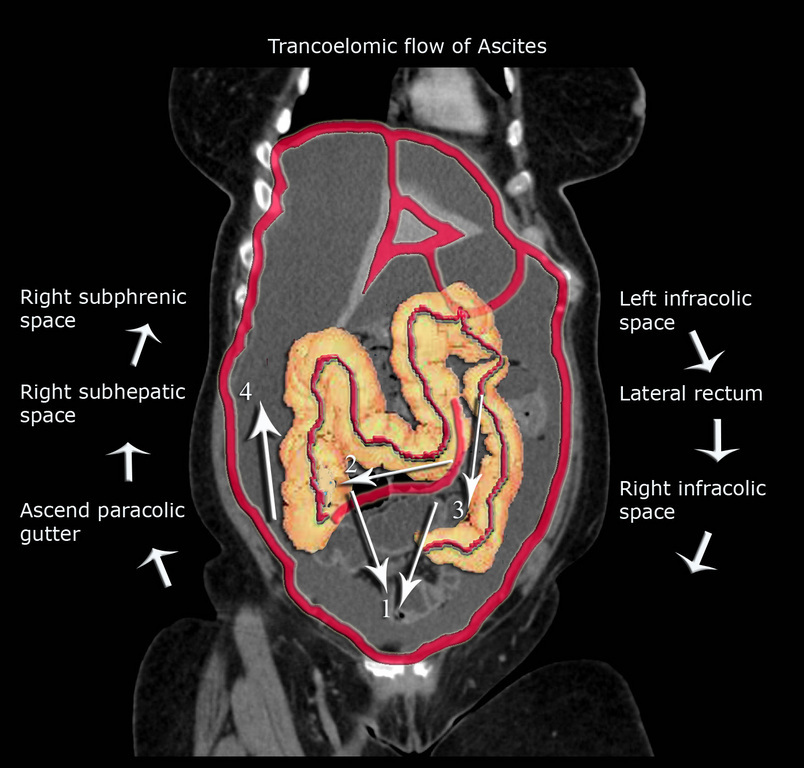
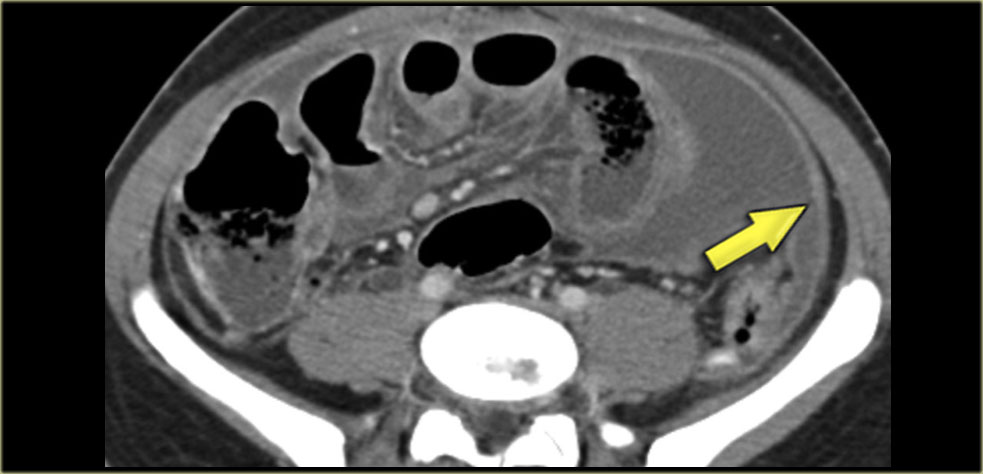
Fluid in the pelvis may ascend the left paracolic gutter 5 but is stopped by the phrenicocolic ligament pcl.
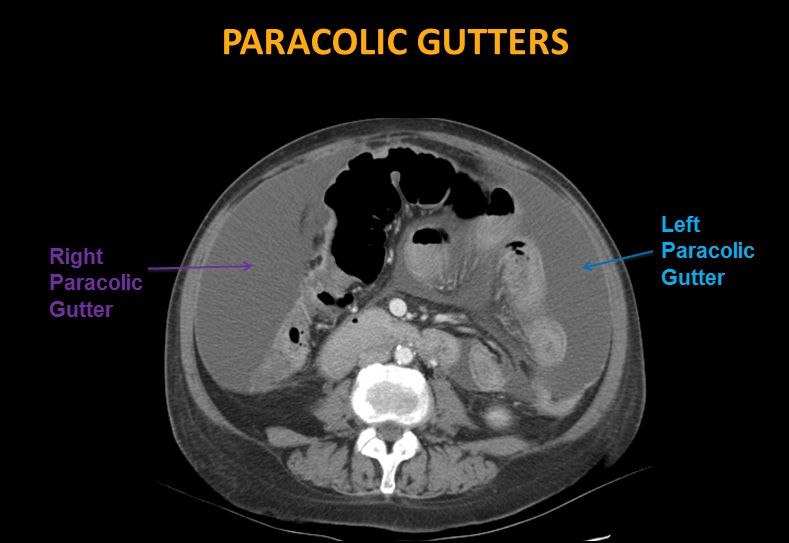
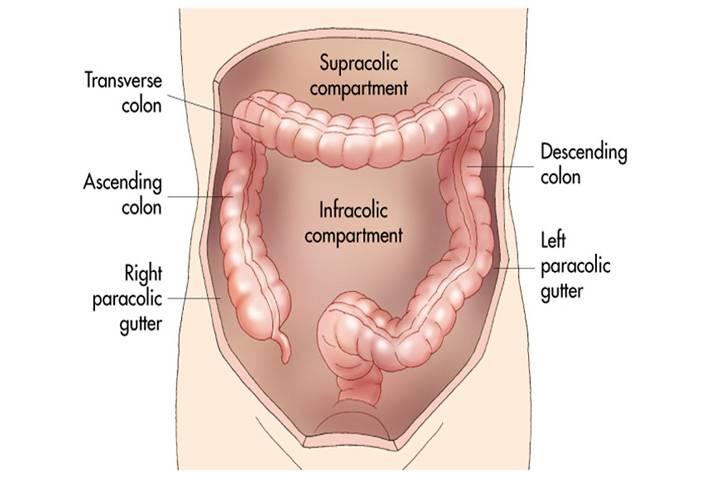
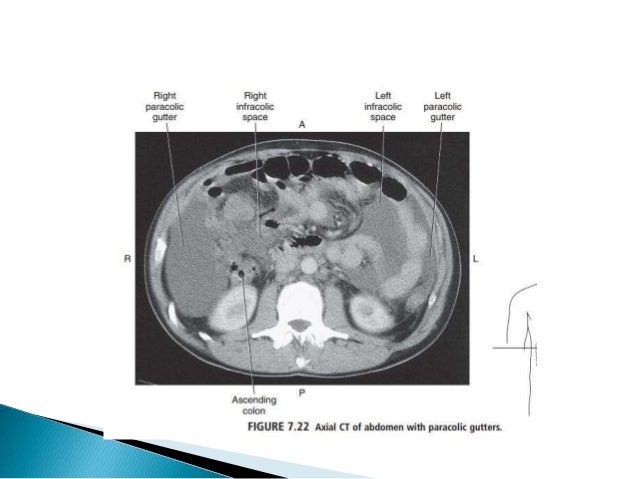
The right and left paracolic gutters are peritoneal recesses on the posterior abdominal wall lying alongside the ascending and descending colon.
A less obvious medial paracolic gutter may be formed especially on the right side if the colon possesses a short mesentery for part of its length.
The right and left paracolic gutter are connected to subphrenic spaces proximally and to the pelvic area at the distal end.
It is seen at the lateral fusion of anterior and posterior perirenal fasciae at the level of the ascending and descending colons.
The right and left paracolic gutters are peritoneal recesses on the posterior abdominal wall lying alongside the ascending and descending colon.
Fluid in the right paracolic gutter 6 ascends to morison s pouch 7 and then to the subphrenic space 8 where it is stopped at the bare area ba of the liver l.
It can be seen in ct on axial cuts.
The left medial paracolic gutter.
The phrenicocolic ligament is a relative but incomplete impediment to the spread of pathologic processes from the left paracolic gutter to the left subphrenic space.
Right supramesocolic spaces the right supramesocolic spaces include the right subphrenic subdiaphragmatic space the morison pouch subhepatic or hepatorenal space and the lesser sac omental bursa.
The main paracolic gutter lies lateral to the colon on each side.
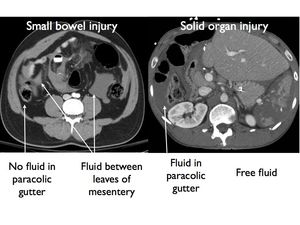
Infected peritoneal fluids get a passageway through these gutters to other compartments of the abdominal cavity.
It has a variable length and can be seen at a level just below the liver or spleen 2.
Using peristaltic motion the carcinomatosis follows the peritoneal circulation and implants along the paracolic gutter passing back up into the undersurface of the diaphragm becoming implanted in morison s pouch the omental bursa and along the left paracolic gutter.
Key signs of peritoneal carcinomatosis.
A less obvious medial paracolic gutter may be formed especially on the right side if the colon possesses a short mesentery for part of its length.